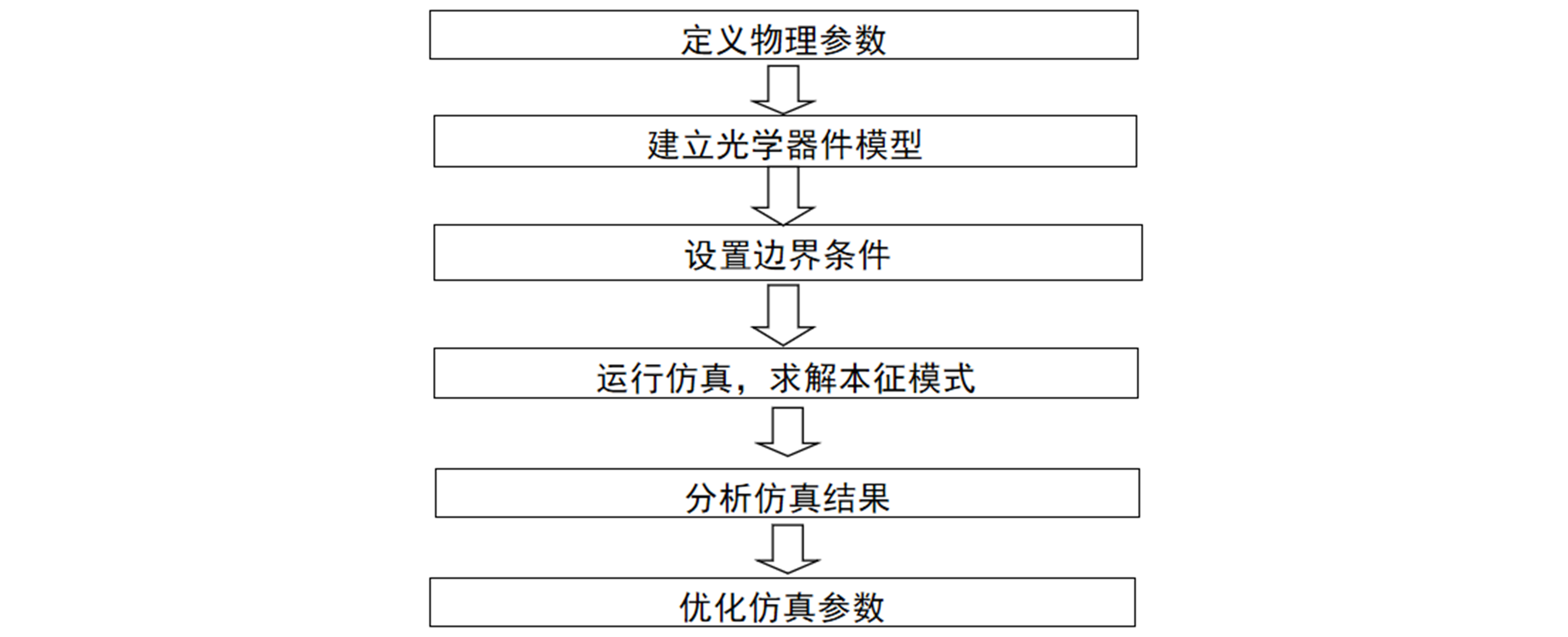
What is the process of simulation?
FDE
The Finite Difference Eigenmode (FDE ) is a numerical solution algorithm that discretizes the Maxwell equations and solves the constructed feature matrix. The solution process for FDE is as follows.
- Calculate the propagation of electromagnetic waves and the field distribution of harmonic modes with high accuracy.
- The calculation cost is relatively low.
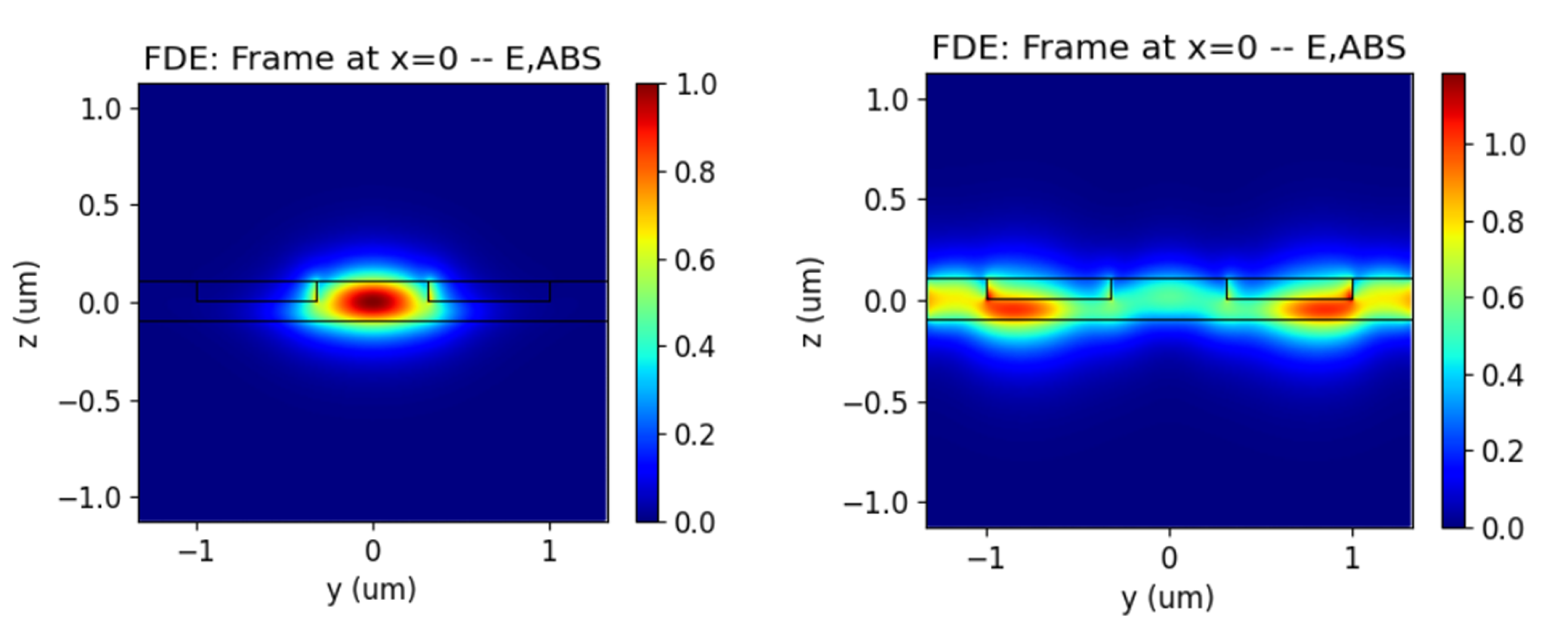
The mode profile of the waveguide using FDE is shown in the following figure.
EME
The Eigenmode Expansion Method (EME) calculates the bidirectional transmission of interface modes in partitioned units to obtain the transfer matrix, which has significant advantages over FDTD in simulating length scanning photonic devices.

- Calculate the transmission characteristics of the device and quickly scan and optimize the device.
- Compared to FDTD methods, the treatment of nonlinearity and dispersion equivalence has certain disadvantages.
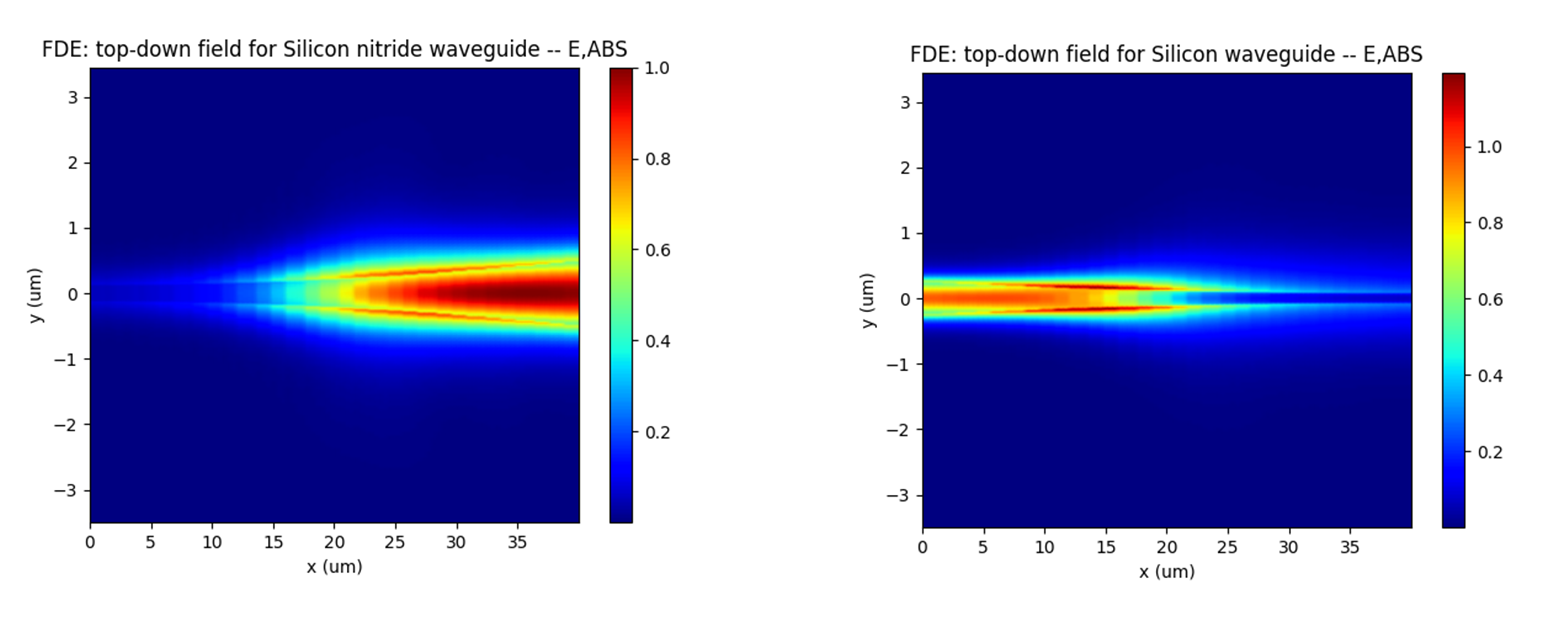
Calculate the electric field distribution of silicon waveguide and silicon nitride waveguide using EME, as shown in the following figure.
FDTD
Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) represents the solution of a partial differential equation as discrete points in time and space, and then uses finite difference to solve the partial differential equation.The simulation process of FDTD is as follows.
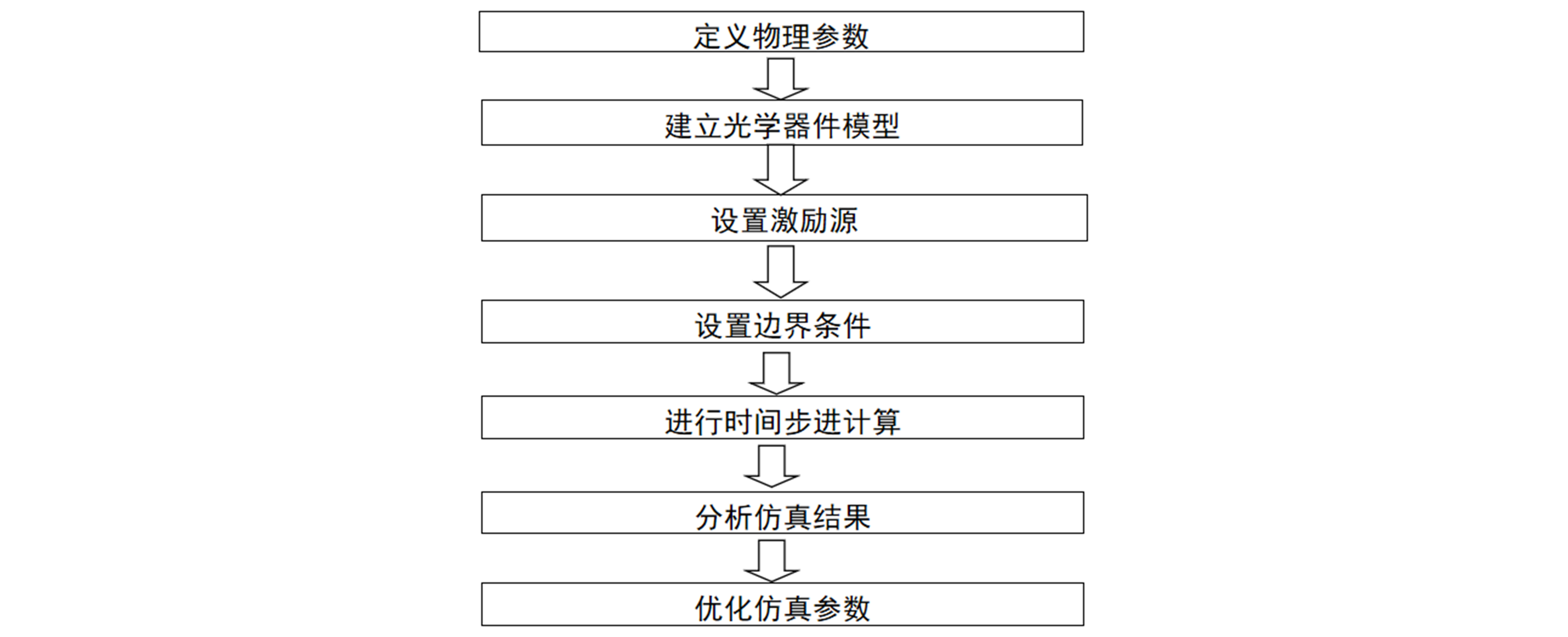
- No approximation was used when solving partial differential equations.
- By using time-domain solutions, it is convenient to observe the propagation of light.
- Obtain the broadband response of the device through a single calculation in the time domain.
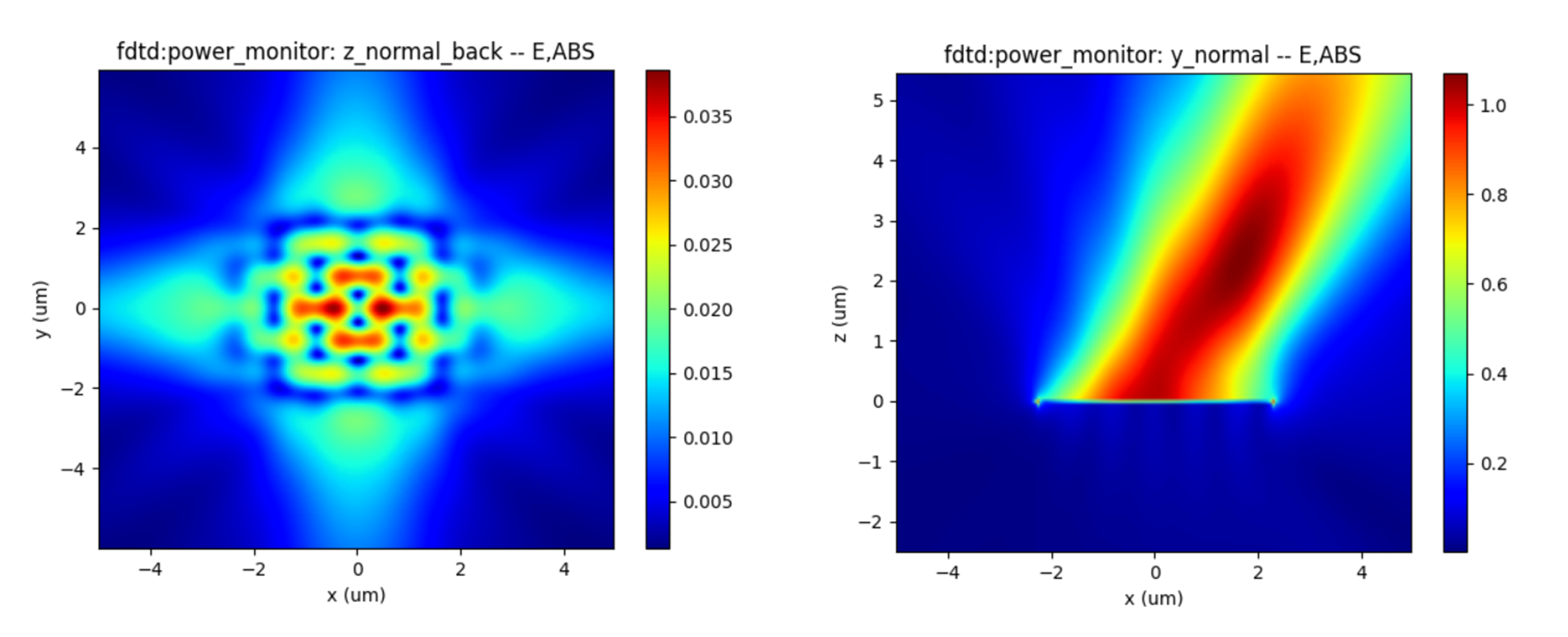
Using FDTD to calculate light field transmission, the electric field distribution in the power monitor is shown in the following figure.